1. a) i) Explain what is meant by the term partition coefficient?
ii) State four conditions under which partition law is valid
b) i) Describe an experiment to determine the partition coefficient of iodine between ether and water
ii) Give four reasons why ethoxyethane (ether) is most commonly used in solvent extraction of organic compounds from their aqueous solution
c) The partition coefficient of a substance Z between methylbenzene and water is 12. Calculate the mass of Z that will be extracted from 200cm3 of an aqueous solution containing 8.0g of Z, by:
i) shaking with 50cm3 of methylbenzene.
ii) Shaking successively with two separate 25cm3 – portions of methylbenzene
iii) comment on your answers in (i) and (iii)
d) State two applications of partition law other than solvent extraction.
2. a) The boiling points of 2-chlorobutance and 2-iodobutane are 680C and 1190C respectively. When treated separately with aqueous sodium hydroxide, followed by acidified silver nitrate solution, 2-chlorobutane forms a white precipitate after about 15minutes, whereas 2-iodobutane forms a white precipitate almost immediately.
Explain;
i) Why the boiling point of 2-chlorobutane is lower than that of 2-odobutane.
ii) The formation of the white precipitate in 2-chlorobutane takes a longer time than in 2-iodobutane
b) Write;
i) equation for the reaction of 1-chlorobutane with aqueous sodium hydroxide
ii) the mechanism for the reaction in (b) (i)
c) The reaction in (b) (i) is exothermic. Sketch a labeled potential energy versus reaction co-ordinate diagram for the reaction.
d) i) Write equation for the conversation of benzene of chlorobenzene
ii) Outline a mechanism for the reaction in (d) (i)
e) Write equation(s) to show how 2 – bromobutane can be converted to butanone.
f) i) Name one reagent that would be used to confirm the formation of butanone
ii) State what would be observed if butanone was present.
iii) Write equation for the reaction of butanone and the reagent you have named in (f) (i)
g) A solution containing iodine and sodium hydroxide was added to hutanone. State what was observed.
3. a) The atomic numbers of scandium and manganese are 21 and 25 respectively. Write the electronic vonfiguration of:
i) Scandium
ii) Manganese
iii) Scandium (III) ion
iv) Maganese(VII) ions
b) Explain why scandium only forms compounds in which its oxidation state is +3, while manganese forms compounds in which its oxidation states are +2 and +7
c) Potassium hydroxide was fused with manganese(IV) oxide in the presence of oxygen to form a green solid X. Solid X dissolved in water to form a green solution. On bubbling carbon dioxide gas through the green solution, a purple solution Y and a brown solid were formed
i) Name solid X and write equation for the reaction leading to the formation of X
ii) Write equation leading to the formation of solution Y
d) When sulphur dioxide was bubbled through acidified solution Y, the color of the solution turned from purple to colorless. Explain.
e) State ehat would be observed and write equation for the reaction that would take place if to the resultant solution in (d) was added;
i) dilute sodium hydroxide solution
ii) acidified barium nitrate solution.
4.a) i) Define the term standard enthalpy change of a reaction .
ii) Briefly, describe how the enthalpy of neutralization of nitric acid by sodium hydroxide can be determined
iii) Explain why the enthalpy of neutralization of sodium hydroxide by nitric acid is 57.1kJmol-1 whereas the enthalpy of neutralization of sodium hydroxide by hydrocyanic acid is 12.0kJmol-1
b) The heat change that takes place when one mole of gaseous ion is completely dissolved in enough solvent is called hydration energy.
State the factors that affect hydration energy and explain their effects.
c) The standard enthalpies of hydration and lattice energies of lithium chloride and potassium chloride are given in a table below.
|
Salt |
Lattice energy |
Hydration energy |
|
Potassium chloride |
-862 |
-883 |
|
Lithium chloride |
-718 |
-695 |
i) Calculate the enthalpy of solution of lithium chloride and potassium chloride
ii) State which one of the two salts would be more soluble in water at a given temperature and give a reason for your answer.
d) Using the thermo chemical data below, determine the lattice energy of sodium chloride.
Using the thermo chemical data below, determine the lattice energy of sodium chloride.
Heat of atomization of sodium = 108 kJmol-1
Dissociation energy of chlorine = 242.2 kJmol-1
Ionisation energy of sodium = 500 kJmol-1
Electron affinity of chlorine = -364 kJmol-1
Enthalpy of formation of sodium chloride = -411.3 kJmol-1
5.a) Carbon, silicon, tin and lead are some of the elements in group (IV) of the Periodic Table.
Discuss the reactivity of the elements with;
i) water
ii) sodium hydroxide solution
iii) concentrated sulphuric acid
b) State what would be observed and write equation for the reaction that would take place if excess concentrated hydrochloric acid was mixed with lead(IV) oxide and heated.
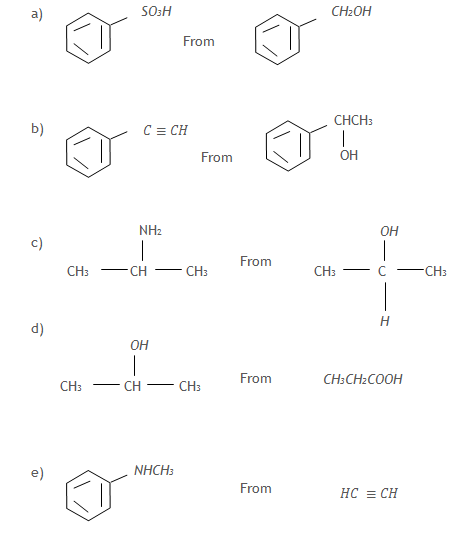
6. Write equations to show how the following compounds can be synthesized
7. a) Define the term eutectic mixture?
b) Briefly, describe hoe a phase diagram of a mixture of biphenyl and naphthalene can be determined in the laboratory.
c) The table below shows the melting points of various mixtures of naphthalene – biphenyl.
|
Mole fraction of naphthalene |
0.125 |
0.275 |
0.450 |
0.625 |
0.800 |
|
Melting point (0C) |
58.0 |
47.0 |
40.0 |
53.0 |
68.0 |
i) Draw a fully labeled diagram of the naphthalene – biphenyl system.
(The melting of naphthalene and biphenyl are 800C and 710C respectively)
ii) Determine the eutectic temperature and the composition of the eutectic mixture.
d) Describe the changes that would take place if a liquid mixture of the above system containing 80% biphenyl was cooled from 850C to 300C.
e) Explain what would be observed when increasing quantities of biohenyl are added to naphthalene
8. Explain each of the following observations and where applicable illustrate your answer with equation(s):
a) Hydrogen sulphide is a gas at room temperature whereas water is a liquid under similar conditions.
b) When a cold mixture of sodium nitrite and concentrated hydrochloric acid solution is added separately to ethylamine and phenylamine, bubbles of a colorless gas are produced with ethylamine but phenylamine only forms a colorless solution.
c) When hydrazine (NH2NH2) is added to an acidified solution of potassium manganate (VII), the potassium manganate(VII) solution turns from purple to colorless and a colorless gas is evolved.
d) When a limited amount of chlorine is added into sodium thiosulphate solution, a yellow precipitate is formed
END
