SECTION A
1. The equation for respiration of a substrate is
2C51H98O6 + 145O2(g) 102CO2(g) + 98H2O(l)
What is the respiratory quotient of the substrate?
A. 0.70
B. 0.80
C. 0.90
D. 1.0
2. If a new born baby suffers from haemolytic disease, it means that the
A. mother is rhesus positive
B. father is rhesus negative
C. baby is rhesus negative
D. father is rhesus positive
3. Which one of the following is true of ammonia as a nitrogenous waste? It
A. requires little energy for its excretion
B. requires much water for its excretion
C. is excreted in a solid form
D. is executed by sea animals
4. Which one of the following would be the effect of increasing the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood?
A. Increase in the ventilation rate
B. Variation of ventilation rate
C. Reduction in ventilation rate
D. Ceasation of ventilation
5. Flowers of the same type were subjected to different temperature and light conditions and they responded as shown in Table 1
Table 1
|
Light intensity (arbitrary units) |
Temperature (0C) |
Flower Response |
|
20 20 30 |
25 30 25 |
Closes Closes Opens |
This shows that the opening of flowers is stimulated by
A. both light and temperature
B. high light intensity
C. low light intensity
D. low temperature
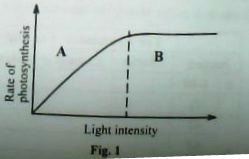
6. Figure 1 shows the variation of the rate of photosynthesis with light intensity.
The factor limiting the rateof photosynthesis in region A is
A. light intensity
B. carbon dioxide concentration
C. water
D. temperature
7. A rigid cuticle of an insect allows some movement because
A. it is made of chitin which makes the limbs flexible
B. during molting enzymes dissolve the old cuticle as a new one is formed
C. the over lapping plates of the cuticle are not continuous at the joints
D. the exo skeletion is periodically shed off for the insect to move
8. In plants, ripening of fruits and falling of leaves are respectively caused by
A. auxins and gibberellins
B. cytokinins and auxins
C. gibberellins and florigen
D. ethene and abscisic acid
9. The onset of depolarization of an axon occurs when the axoplasm temporarily becomes
A. more negative
B. Oxygen levels
C. Lichen diversity
D. Humidity levels
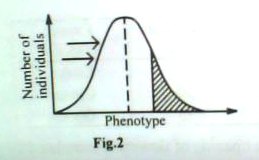
10. Which one of the following would happen to individuals of the population in the shaded area of figure 2 if selection pressure continued for generations acting on the phenotype?
They would
A. develop into two distinct populations
B. die off and becomes extinct
C. evolve into new species
D. multiply in number
12. Starch and glycogen are suitable storage molecules because they
A. are large in size which makes them less soluble in water
B. are chemically reactive in the cell
C. can easily be hydrolysed
D. exert an osmotic pressure in the cell.
13. In which one of the following structures of a moss does meiosis occur?
A. Gametophyte
B. Sporopyte
C. Archegonium
D. Antheridium
14. A total of 180 black jack plants were recorded after throwing a 2m2 quadrat 30 times in an area of 160,000m2. The estimated number of black jack plants in the area were
A. 53,333
B. 192,000
C. 480,000
D. 960,000
15. Two cells A and B have water potentials of -2000kPa and -1000kPa respectively. Which one of the following statements is true about the cells?
A. Cell A has a higher concentration of water molecules than cell B
B. Cell A has a higher solute potential than cell B
C. There is a net movement of water from cell A to cell B
D. Cell A has a less solute concentration than cell B
16. Whichone of the following is the role of the capillary network around the alveoli in mammals?
A. Makes the alveoli more permeable
B. Increases the surface area of the alveoli
C. Maintains a steep diffusion gradient
D. Makes the alvel movement of water from cell A to cell B
D. Cell A has a less solute concentration than cell B
16. Whichone of the following is the role of the capillary network around the alveoli in mammals?
A. Makes the alveoli more permeable
B. Increases the surface area of the alveoli
C. Maintains a steep diffusion gradient
D. Makes the alvel movement of water from cell A to cell B
D. Cell A has a less solute concentration than cell B
16. Which one of the following is the role of the capillary network around the alveoli in mammals?
A. Makes the alveoli more permeable
B. Increases the surface area of the alveoli
C. Maintains a steep diffusion gradient
D. Makes the alveoli cell thinner
17. Which one of the following organelles would be most abundant at a site where some embryonic tissues are being discarded?
A. Mitochondria
B. Ribosomes
C. Golgi apparatus
D. Lysosomes
18. Gaseous exchange in earthworms occurs at the body surface because the body is
A. moist
B. elongated
C. segmented
D. flattened
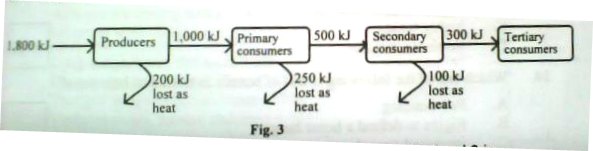
19. Figure 3 shows energy transfer in an ecosystem
The percentage of energy used for other activities in trophic level 2 is
A. 25%
B. 50%
C. 75%
D. 100%
20. Which one of the following properties of water enables its movement through the apoplast pathway in a plant?
A. High latent heat of vapourisation
B. Polarity of its molecules
C. High adhesion – cohesion forces
D. High surface tension
21. Which one of the following conditions would lead to the Bohr effect in a mammal?
A. Decrease in the pH of the blood
B. Increase in the partial pressure of oxygen in the environment
C. Decrease in the metabolic rate
D. Increase in environmental temperature
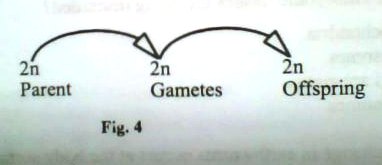
22. Which one of the following can be concluded from the reproductive process in figure 4?
The
A. process occurs fat
B. offspring are identical
C. offspring are many
D. offspring are resistant
23. Some animals living in arid habitats excrete uric acid because it is
A. not toxic
B. highly soluble in water
C. highly toxic
D. insoluble in water
24. Which one of the following is not if benefit in territorial behavior?
A. Pair bonding
B. Rights to defend a home range
C. Increased reproductive success
D. Saving energy used to chase away invaders
25. A partially closed ductus arteriosus in an individual causes
A. high blood pressure
B. shortage of oxygen to tissues
C. heart attack
D. anaemia
26. Which one of the following chromosomal mutations causes Down’s Syndrome?
A. Non-disjunction
B. Deletion
C. Inversion
D. Duplicaiton
27. Which one of the folloeing is the correct state in the guard cells in relation to the neighbouring cells, when the stoma opens?
A. Low PH
B. Sugar being converted to starch
C. Little acid present
D. Higher water potential
28. A fresh water bony fish solves its osmoregulatory problems by
A. possessing few glomeruli
B. having a long loop of henle
C. possessing many glomeruli
D. actively secreting salts into water
29. Which one of the following is the major form in which carbon dioxide travels to the lungs from tissues?
A. Carbonic acid
B. Sodium bicarbonate
C. Carboxyhaemoglobin
D. Bicarbinate ions
30. In Drosophila, the alleles for width of abdomen and length of wings are linked. When a Drosophila with long wings and broad abdomen was mated with one possessing vestigial wings and narrow abdomen, the following offspring were obtained:
Long winges, broad abdomen = 686
Long wings, narrow abdomen = 211
Vestigial wings, broad abdomen = 206
Vestigial wings, narrow abdomen =465
What was the cross over value?
A. 13.3%
B. 26.6%
C. 49.4%
D. 73.4%
31. If the magnification of a microscope is 50,000 times and the size of the image viewed is 5mm, the actual size of the object is
A. 1 × 10-4μm
B. 0.01 μm
C. 0.1 μm
D. 1.0 μm
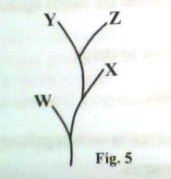
32. Figure 5 shows the relationship between four different species W, X, Y and Z
Which pair of the species would have the least competition for resources if they lived together?
A. X and Y
B. X and W
C. Y and Z
D. Z and W
33. Which one of the following is not true of a contracted muscle fibre?
A. M-line shortens
B. Sarcomere shortens
C. H – zone shortens
D. Light bands shorten
34. Which one of the following describes facilitated diffusion?
A. Molecules are moved by protein carriers from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
B. Water molecules move across a semi- permeable membrane
C. Molecules move from a region of high to low concentration
D. Energy is used when molecules are moved across a cell membrane
35. Larval forms and their adults do not come into direct competition because the larvae
A. are independent organisms
B. are different in structure and feeding habitats
C. have restricted mobility
D. reproduce asexually
36. The most important adaptation of a plant in a salty environment is possession of
A. deep roots
B. root hair sap with low water potential
C. many superficial adventitious roots
D. tissues with large air spaces
37. Which one of the following is the major cause of slow growth of a population of individuals when they have just migrated to a new area?
A. Insufficient food in the new area
B. Pressure from many predators
C. Small numbers of reproducing
D. Diseases which kill many individuals
38. which one of the following changes of activities occur when adrenaline is released in a mammalian body?
A. Reduction in oxidation of glucose
B. Conversion of glucose to glycogen
C. Conversion of fat in adipose tissue into glucose
D. Increase in the uptake of glucose by tissue cells
39. Which one of the following actions in photosynthesis is most affected by low temperature?
A. Absorption of light
B. Splitting of water
C. Fixation of carbon dioxide
D. Formation of ATP
40. Which one of the following is true about the state of the axon membrane during the absolute refractory period? It is
A. depolarized
B. inexcitable
C. polarized
D. excitable with a stimulus stronger than usual
SECTION B
41. Table 2 shows the relative contribution of aerobic and anaerobic respiration to the total energy output in an individual during exercise
Table 2
|
Duration of exercise (min) |
Relative contribution of energy (%) |
|
|
From aerobic respiration |
From anaerobic respiration |
|
|
0.5 2.0 10.0 60.0 |
83 40 9 1 |
17 60 91 99
|
a) Compare the relative contribution of aerobic and anaerobic respiration to the total energy output, with duration of exercise
b) Explain the changes in the relative contributions of aerobic and anaerobic respiration with duration of exercise
c) Explain why diving mammals have reduced heart beat rate.
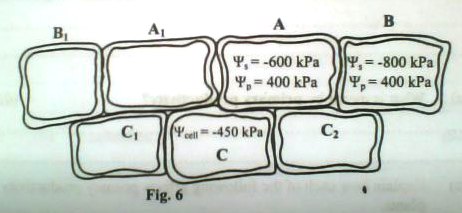
42. Figure 6 shows two guard cells A and A1, with adjacent cells B, B1, C, C1 and C2. The values of the solute potential and pressure potential; shown in cells A and B are exactly the same as those for cells A1 and B1 respectively. Similarly, the water potential indicated in cell C is the same as that in cell C1 and C2. Use the figure to answer the questions that follow.
a) i) Calculate the water potential of cells A and B
Cell A
Cell B
ii) Show by means of arrows the net movement of water in the seven cells
b) Explain why the net movement of water in the cells is as you have indicated in (a) (ii)
c) What would be the effect of the net movement of water indicated in (a) (ii) to guard cells A and A1?
43. a) What is meant by primary productivity?
b) Explain how each of the following affects primary productivity in plants.
i) Water stress
ii) Chlorosis
44. a) Explain the function of antigens and antibodies in the immune sytem.
i) Antigens
ii) Antibodies
b) State two ways in which passive immunity may be acquired naturally by a young child.
c) During vaccination against tuberculosis (T.B), children are injected with a weakened strain of T.B bacteria. Explain how this procedure can result in long term defence against T.B
45. a) Distinguish between continuous and discontinuous variation
b) Explain how each of the following causes variation in sexually reproducing organisms
i) Crossing over during meiosis
ii) Independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis
46. a) What is meant by inhibition of an enzyme?
b) Explain how an end-product inhibition in an enzyme controlled reaction is a negative feedback.
c) Explain the role of the active sites of n enzyme in enzyme specificity.