1. a) i) State the kinetic theory of matter
ii) Describe how solids, liquids and gases differ
b) Describe an experiment to show the existence of surface tension in liquids
c) When a scale pan is fitted to a spring with a pointer, the pointer points to 30cm mark on a meter rule. When sugar is added onto the pan, the pointer points on 15cm mark. When a 0.02 kg mass is put on the sugar, the pointer points on 5cm mark. Calculate the mass of the sugar.
d) i) Explain why steel is used as a construction material
ii) State two advantages of concrete as a building material
2. a) i) What is meant by energy
ii) State the principle of conservation of momentum
b) Define;
i) potential energy
ii) kinetic energy
c) Explain the energy changes that take place when a generator running on petrol is used to generate electricity
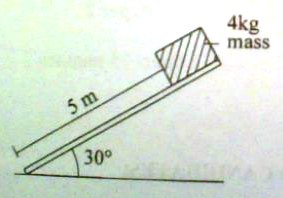
d) A block of mass 4kg is released from rest at the top of a smooth plane 5m long and inclined at 300 to the horizontal as shown below.
Find the;
i) change in potential energy when the block reaches the bottom of the plane
ii) velocity of the mass at the bottom of the plane
e) Briefly describe one application of the law of conservation of momentum
3. a) i) State Archimedes’ principle
ii) Describe an experiment to verify Archimedes’ principle
b) i) Explain why a hydrometer is made with its bulb wide and its stem narrow
ii) State two examples where a hydrometer is commonly used.
c) A spring balance reads 9.0N when a solid metal ball is suspended from it in air. The density of the metal is 6.25gcm-3 and that of water is 1 gcm-3. If the ball is lowered into water in a measuring cylinder until it is completely immersed, find the
i) volume of water displaced
ii) reading of the spring balance
4. a) Define wavelength of a water wave
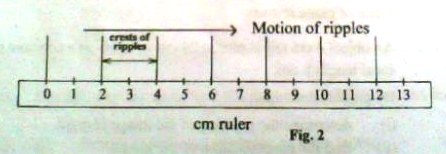
b) Figure 2 shows the position of crests of ripples in a ripple tank
i) Determine the wavelength of the ripples
ii) If the frequency of the ripples is 15Hz, calculate the velocity of the ripples
c) Describe an experiment to measure the velocity of sound in air
d) Explain why it is very difficult to hear someone speaking clearly in a large hall which has no soft lining on the walls and no cushioned chairs
e) State two factors which affect the speed of sound
f) Distinguish between pitch and loudness of sound
5. a) State the laws of refraction of light
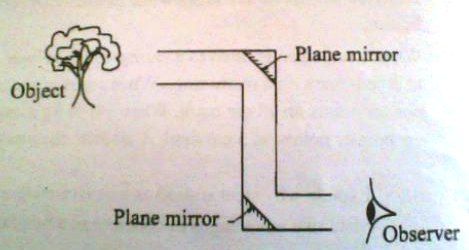
b) Figure 3 shows a periscope being used to view a distant object by an observer
Copy the diagram and show how the image of the object appears to the observer
c) Give two reasons why a periscope made of prisms is better than one made of plane mirrors
d) An object 4cm tall is placed 24cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 8cm
By graphical method;
i) determine the position
ii) find the magnification of the image
iii) state the nature of the image
e) Give two uses of concave mirrors
6. a) i) What is magnet
ii) Why are keepers made of soft iron?
iii) State two ways by which a magnet may lose its magnetism
b) Wuth the aid of a diagram, describe how a loud speaker works
c) What is meant by electromotive force (e.m.f) of a cell?
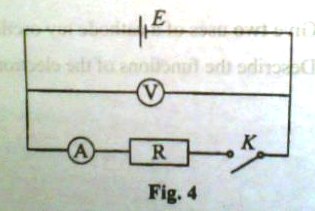
d) A dry cell with e.m.f, E, is connected in a circuit as shown in figure 4
When switch K is open, the voltmeter reading is 1.4V. When switch K is closed, the ammeter reading is 1.0A and the voltmeter reading is 0.9V.
i) Write an expression relating, E, ammeter reading, I, voltmeter reading, V, and the internal resistance of the cell.
ii) Calculate the internal resistance of the cell
iii) Find the value of the resistance, R
7.a) State the use of the following in writing a building
i) The fuse
ii) The switch
iii) The earth connection
b) Explain why the space in a filament lamp is filled with an inert gas.
c) i) Briefly explain the operation a d.c motor
ii) How can the power of a motor be increased?
iii) An electric water pump raises 0.9kg of water through 20m every second. If the efficiency of the pump is 90%, calculate the power supplied to the motor.
8. a) What is meant by;
i) a radioactive nuclide?
ii) back ground radiation?
b) State three precautions taken while handling radioactive materials
c) List two applications of radioactivity
d) Explain one application X-rays
e) i) Give two uses of a cathode ray oscilloscope (C.R.O)
ii) Describe the functions of the electron gun in a C.R.O
END